Follow-along: Define tools with local operations (⏳ 10 min)
🎯 Goal: Expose your GraphQL operation as an MCP tool.
Step 1: Define a new tool for your agent
In your Sandbox at http://localhost:4000/ you should still have the query you designed from the previous step. This query will become your MCP tool!
Add a description above your tool.
Example description# Get the last 5 launches with current weather on the launchpadMCP tool descriptions give the agent all the context they need about the tool including variables, datatypes, and any limitations. When you write a description, you should consider what the agent needs to know to effectively use your tool.
Find out more about writing tool descriptions in the section below.
Look for other opportunities to give your agent better context through field aliasing. For example,
launchIdas a variable name gives your agent more information thanid.Rename your operation to be more descriptive, for example
GetLastFiveLaunches.Here is an example of what our agent-ready operation looks like. Yours may look different.
Example operation# Gets upcoming launches with pad visibilityquery GetUpcomingLaunchesWithPadVisibility(# The number of launches to return, not to exceed 10$limit: Int = 5) {upcomingLaunches(limit: $limit) {idnamepad {nameweather {visibility}}}}
Step 2: Save the tool locally
- In your project, create a folder called
tools. - In this folder create a graphql file with the same name as your tool. For example,
GetLastFiveLaunches.graphql. - Copy the operation from Step 1 above into this file and save it.
Step 3: Run your project as an MCP Server
To test the MCP server, we'll use the MCP Inspector.
Note: You can also use Postman to test your MCP Servers.
Exit goose using
CTRL + C.Run this script to kill your open port:
lsof -t -i :4000 | xargs kill -9We are going to start rover with MCP enabled this time. Run this script:
rover dev --supergraph-config supergraph.yaml --mcp mcp-config.yamlOpen a new terminal in your IDE. For VSCode, you can click the + to the top right of your terminal. Run this command to start the MCP Inspector tool.
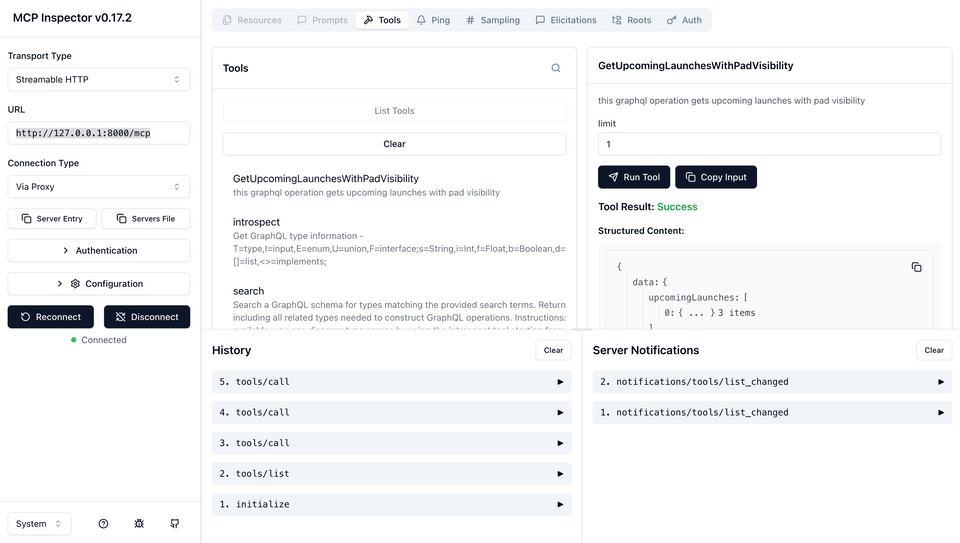
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcp --transport httpOpen the URL from your terminal output in your browser. It should look something like this:
Example terminal outputStarting MCP inspector...⚙️ Proxy server listening on port 6277🔑 Session token: ...Open inspector with token pre-filled:http://localhost:6277/?MCP_PROXY_AUTH_TOKEN=...In the MCP Inspector, on the left sidebar, ensure that the endpoint is set to
http://127.0.0.1:8000/mcpand the transport type is set toStreamable HTTP.Click the
Connectbutton.Click
List Tools. You should see your tool name.Click on the tool name to see the tool details. You may need to add a value for the variable that your operation requires. For example, if your operation requires a
$limitvariable, you may need to add a value for it.Click the
Run Toolbutton to execute the tool.You should see the tool details and the results of the tool execution.
Tips on writing tool descriptions
Tool descriptions help AI agents understand what the tool does and how to best use it. GraphQL's declarative nature and typed schema makes this easy. You can also:
- Provide verbose and clear GraphQL operation names (e.g.
GetFiveRecentIssuesvsGetIssues)) - Add a comment above the operation (prefixed by
#) that says exactly what the tool does and if it requires any parameters. This will override the auto-generated description from your schema.
For more information on writing tool descriptions, check out the following resources:
Tips and troubleshooting
If you update the MCP configuration file, you'll need to restart the MCP server for the changes to take effect.
If your agent fails to run the MCP server or your would like to run it manually, use this command:
rover dev --supergraph-config supergraph.yaml --mcp mcp-config.yamlIn some cases, your agent may have generated a router file. To use this, add the flag
--router-config router.yamlto the command.rover dev --supergraph-config supergraph.yaml --mcp mcp-config.yaml --router-config router.yaml
Practice
- Can you expand on the current
GetLaunchestool to include more fields? - Instead of adding even more to the
GetLaunchestool, use the Sandbox to create a new tool and save it to your tools folder.