Overview
The Listings team has some exciting updates ready to publish to the registry, but they need to be confident in these schema changes before publishing them to the production variant. Fortunately, there's an GraphOS feature to help with that: schema checks!
In this lesson, we will:
- Learn about the different types of schema checks
- Understand how schema checks fit into the overall process of updating a supergraph
- Learn about the launch process in GraphOS
In this lesson, we'll focus mainly on the high-level overview of the process. The next lesson will dive more into the details of how to run each check.
What are schema checks?
Schema checks are a set of predefined tests that help identify potential failures caused by schema updates. They check for issues like incompatibilities between subgraph schemas or breaking existing client operations. With schema checks, we can ensure that our schema changes won't cause issues when we deploy to production.
There are three types of schema checks: build checks, operation checks and linter checks.
Build checks
Build checks validate that a subgraph's schema changes can still compose successfully with other subgraph schemas in the supergraph.

For example, if a new type is added to one subgraph, a build check determines whether that addition is compatible with the rest of the subgraphs in the supergraph. If it isn't, we need to investigate the error and fix it.
Operation checks
Operation checks validate that a schema's changes won't break any operations that existing clients send to the graph.

For example, let's say a web client regularly sends a GraphQL query to retrieve data for its homepage. If a schema change involves adding a required argument to a field in that query, it might break that client's existing operation if it doesn't include that argument! An operation check helps us guard against this potential failure, listing out the affected operations and allowing the team to address them.
Linter checks
Linter checks analyze your proposed schema changes for violations of formatting rules and other GraphQL best practices. GraphOS provides a set of default rules you can configure to suit your team's conventions. You can see a full list of rules in the Apollo documentation.
Some common schema conventions include: writing field names in camelCase, type names in PascalCase, and enums in SCREAMING_SNAKE_CASE.
How to run schema checks
There are two main ways to run schema checks using the Rover CLI. We can run schema checks locally in our terminal. We can also integrate schema checks into our CI pipelines to run automatically against new pull requests.
To perform a schema check for a subgraph, we use the rover subgraph check command with the following parameters:
rover subgraph check <GRAPH_REF> \--schema <SCHEMA_FILE_PATH> \--name <SUBGRAPH_NAME>
Note: The graph reference (or graph ref) tells Rover about our supergraph. A graph ref starts with the graph's ID, followed by an @ symbol, followed by the graph variant.
This command runs a build check first, then an operation check, then a linter check, and finally outputs the results in the command line. It also reports the results to GraphOS, so we can view them from your graph's Checks page.
Schema checks in the supergraph story
Let's revisit our story and zoom in to where schema checks occur and what happens when they fail, pass, or are actively overridden.
After making changes to a subgraph schema (whether that's adding, removing, or updating definitions), we first want to run schema checks locally using Rover.
First, Rover validates that a subgraph's schema changes can still compose successfully with the other subgraph schemas in the supergraph. By default, this check runs against the current variant of the graph, but we can also select any graph variant already registered in Studio.
If the build check succeeds, Rover runs an operation check immediately after. This validates that the schema's changes won't break any operations that existing clients send to the graph.
If either check fails, Rover provides a link to the Studio Checks page that contains more information about what went wrong.
If all the checks are successful, we can go ahead and follow the same process as before: we'll use Rover to publish the subgraph schema to the registry.

While we're on the subject of publishing schema changes, let's take a moment to touch on a useful feature of GraphOS: a launch.
Launch process
By publishing to the schema registry, we've triggered a launch in GraphOS.
A launch represents the complete process of making schema updates to any variant of a graph.
A launch starts with GraphOS attempting to compose the supergraph. If it fails, we'll see an error and the process stops there. Otherwise, a supergraph schema is produced. The supergraph schema is provided to Uplink and the GraphOS Router will fetch the latest schema.
We've successfully completed our schema updates to the graph!
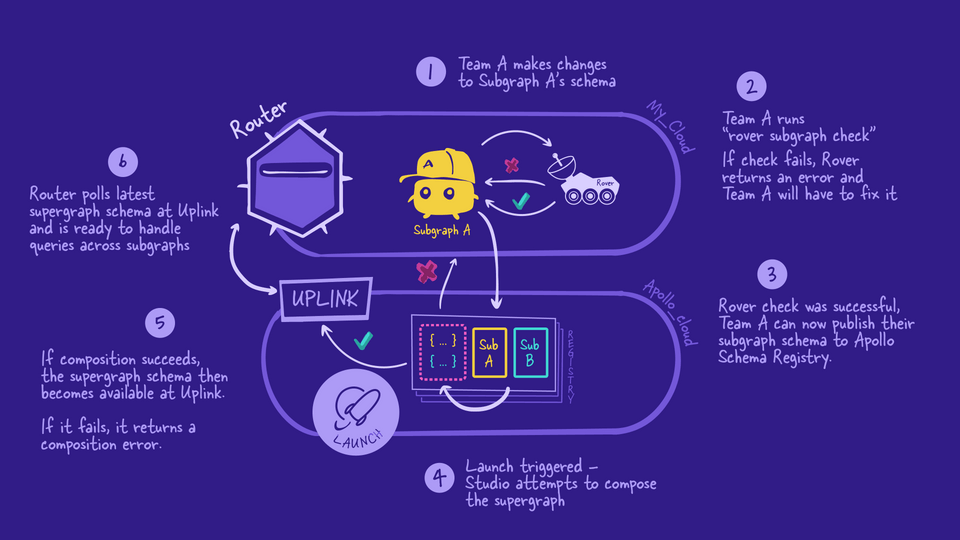
And that's what schema checks and the launch process look like in our supergraph.
Practice
Drag items from this box to the blanks above
Operation
Deprecated
Linter
Field
Build
Subgraph
Key takeaways
- Schema checks help identify potential failures caused by schema updates before they can cause issues in production.
- Build checks validate that a subgraph's schema changes can still compose successfully with other subgraph schemas.
- Operation checks validate that a schema's changes won't break any operations that existing clients are sending to the graph.
- Linter checks validate that a schema follows formatting rules and conventions.
- To run a schema check, we use the
rover subgraph checkcommand. - We can inspect the results of a schema check through the terminal or in the Studio Checks page.
- A launch represents the complete process of making schema updates to any variant of a graph. It's triggered by a subgraph being published to the schema registry.
Up next
In the next three lessons, we'll see how schema checks work in our development workflow and how they can be automated in the CI/CD process.
Share your questions and comments about this lesson
Your feedback helps us improve! If you're stuck or confused, let us know and we'll help you out. All comments are public and must follow the Apollo Code of Conduct. Note that comments that have been resolved or addressed may be removed.
You'll need a GitHub account to post below. Don't have one? Post in our Odyssey forum instead.