Overview
Now for the fun part: actually using our supergraph!
In this lesson, we will:
- Run queries in Apollo Explorer
- Create and use operation collections
Building and running queries
We can easily build, run, and manage GraphQL operations with the help of the Apollo Explorer. The Explorer IDE is part of the GraphOS platform and it's easily accessible through the sidebar navigation.
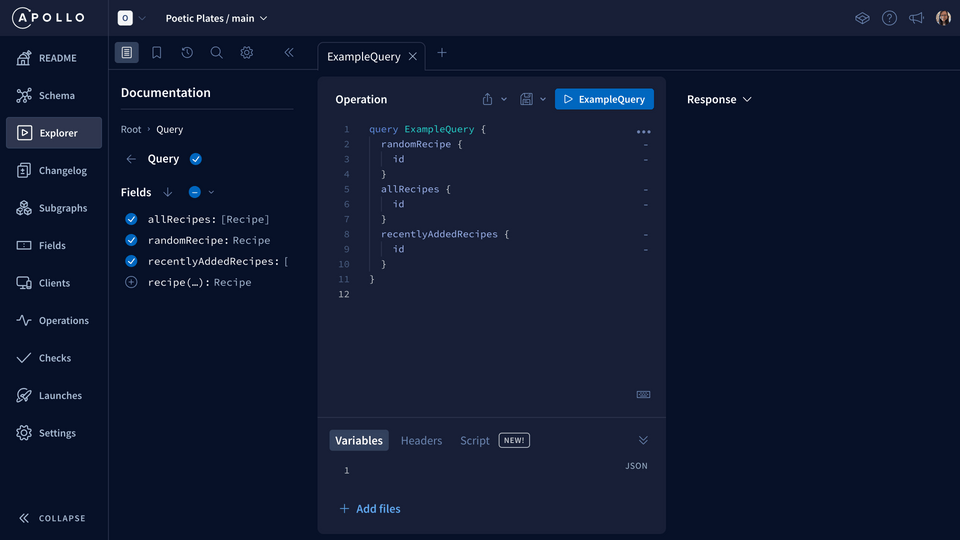
Note: You can also get to the same page immediately after creating your supergraph by clicking on Query your supergraph in the modal.
Let's run our first query.
Getting to know the Explorer
The Operation panel in the middle is where we create queries. The Explorer has already filled in a default operation! You can edit the operation directly or add fields from the Documentation sidebar.
At the top of the Operation panel is the button to run our query. Let's click it now and see what happens!
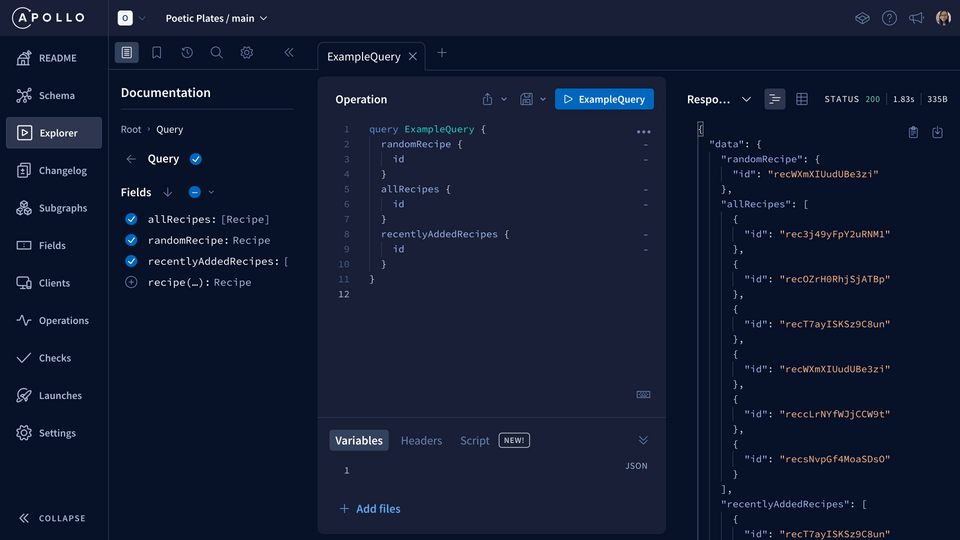
The Response panel on the right displays our list of recipe IDs. Not super helpful right now, so let's spice up this query.
We'll ask for a random recipe and include all the details we need to prepare it.
query GetRandomRecipe {randomRecipe {idnamecookingTimeprepTimeservingsinstructionsreadyTimeingredients {text}}}
When we run this query, we'll get back data about a random recipe, in Poetic Plates style.
We might want to use this query again, so let's save it using operation collections.
Operation collections
There are two types of collections: personal and shared.
Personal collections are visible only to you. Shared collections are visible to all organization members who can view the supergraph the collection belongs to.
Creating a shared operation collection
Let's get our shared collection started, this is going to be helpful for future teammates (and future us!) to get the most out of the supergraph.
Click on the bookmark icon to access your collections.
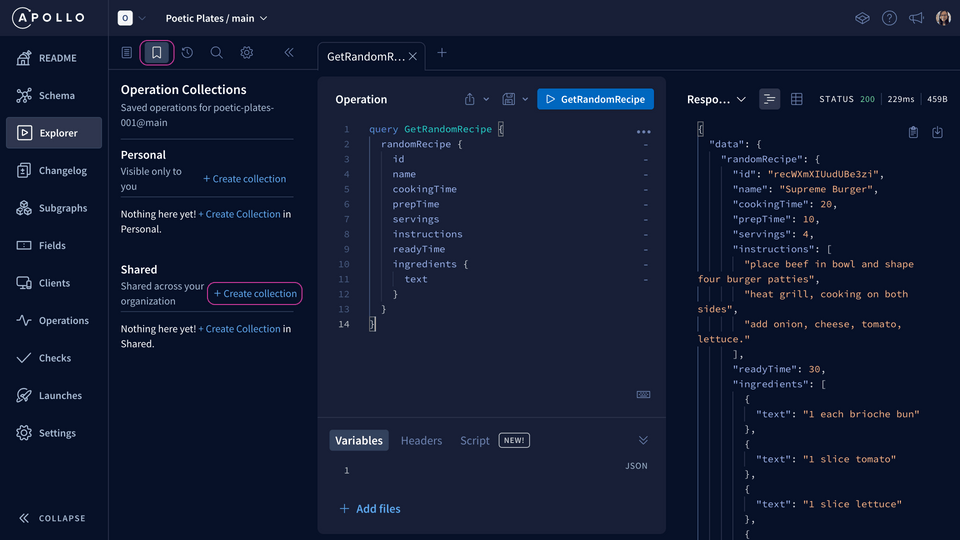
Under the Shared section, click the + Create collection button.
We'll give the collection a name and a description.
Name: RecipesDescription: A collection of queries to retrieve content about recipes
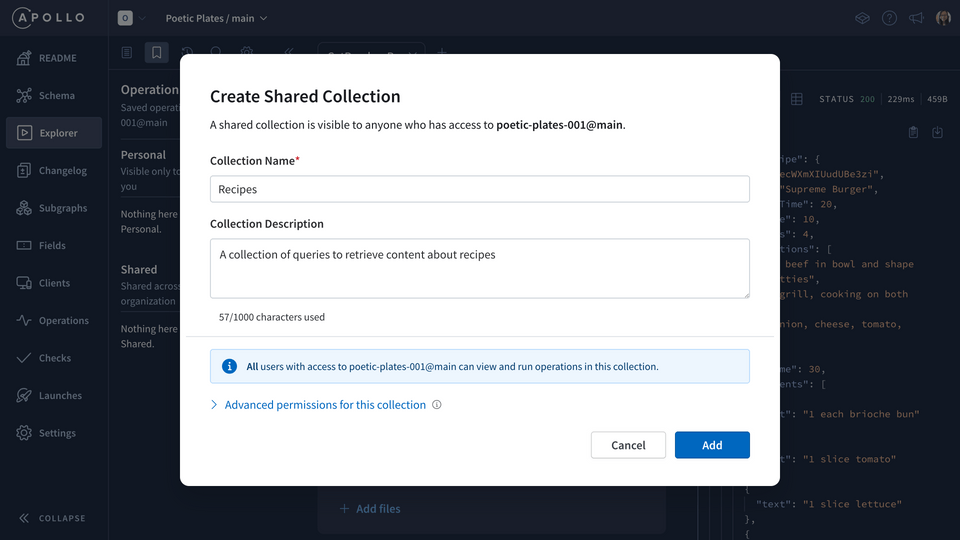
Then click Add. We'll see the new collection show up under the Shared section.
Saving an operation to a collection
Next, let's add to our collection. Click the Save icon.
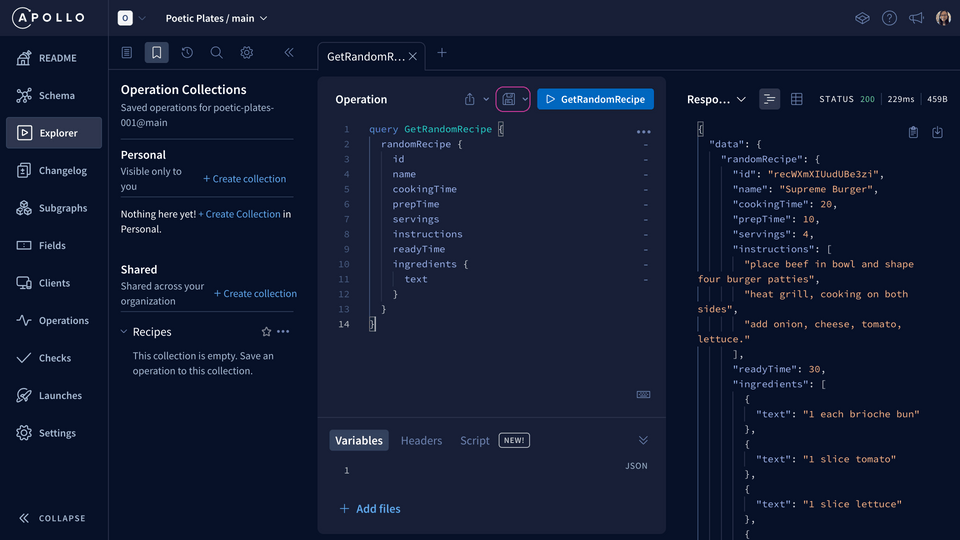
We'll use the same operation name we already gave it. Then, select the collection it belongs to (the one we just created earlier!).
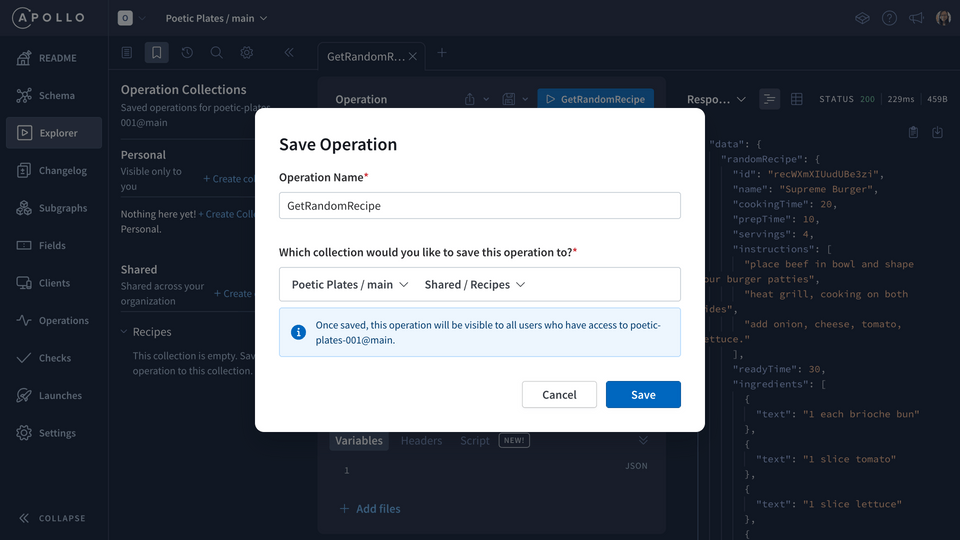
We'll hit Save, and success!
We can see the operation name under this shared collection, and we can see a bookmark icon in the tab that also tells us that this operation is saved. It's ready to use whenever we need it!
Practice
Key takeaways
- Operation collections help you store and organize commonly used operations so you can access them more quickly and share them with team members.
- You can save collections that are visible only for yourself (personal) or visible to the whole organization (shared).
Up next
This is great, we can already send queries to our supergraph! Now let's make sure other people can use it too. In the next lesson, we'll learn a couple ways to enable the best API experience for our users.
Share your questions and comments about this lesson
Your feedback helps us improve! If you're stuck or confused, let us know and we'll help you out. All comments are public and must follow the Apollo Code of Conduct. Note that comments that have been resolved or addressed may be removed.
You'll need a GitHub account to post below. Don't have one? Post in our Odyssey forum instead.