Overview
Poetic Plates is meant to be a public API, ready for anyone to discover and try new recipes, whether it be through a web app, mobile app or another API.
In this lesson, we will:
- Create a public variant to enable anyone to easily build and run queries using Explorer
- Configure the cloud router's CORS policies to accept requests from any origin
Graph variants
Let's start with variants. A variant represents a different environment where the supergraph runs.
For example, we could have a variant for staging or pre-production, a common environment where we can test our schema changes before they go live. We could have another variant for production, which is live and in use by clients.
In GraphOS, each variant of a supergraph has its own schema, metrics, change history, and operation history.
So far, we've been working with only one version of our supergraph: the version that's currently running in production. This is actually our very first variant, which is called main. By default, this variant is private and only visible to members of our Studio organization.
Note: Although we're working in local-land, we're connected to production data. In the real world, you'll probably have a separate supergraph variant to handle local queries and mutations so that production data isn't compromised. You can learn more about graph variants and workflows in the Voyage III course.
We want to allow folks, even outside our organization, to explore the schema freely and send queries using Explorer, so we'll need to make this variant public.
By making a public variant, our API consumers will be able to see these pages:
- Home, which shows the variant's README to help onboard newcomers
- Schema, which shows the types and fields that make up the supergraph.
- Explorer, which enables consumers to build and run queries.
- Changelog, which shows the recent changes to our supergraph.
The pages showing your supergraph's metrics (Fields, Operations) and settings won't be viewable!
Creating a public variant
Let's go ahead and make our main variant public.
Go to our variant's Settings page and open the This Variant tab.
Find the Public card and click Change.
https://studio.apollographql.com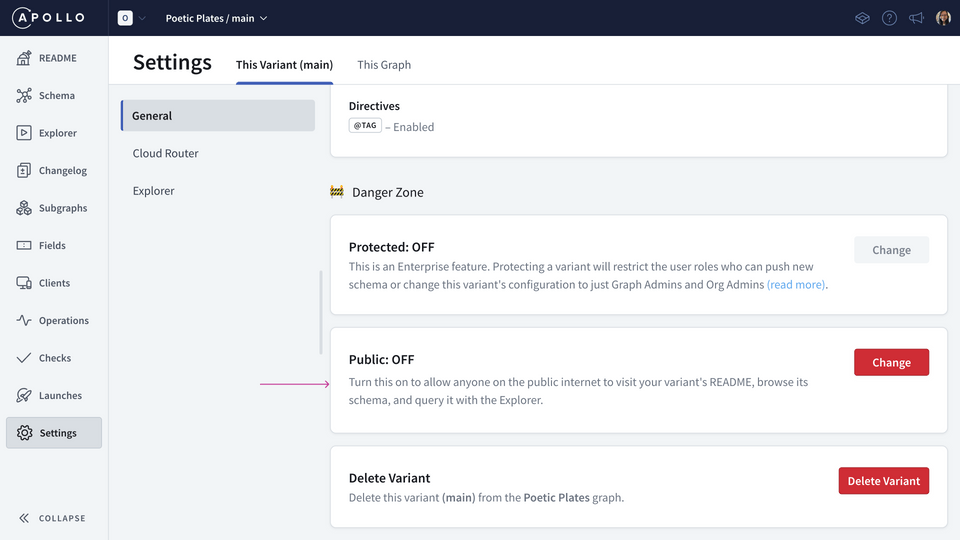
Select On and save our changes.
https://studio.apollographql.com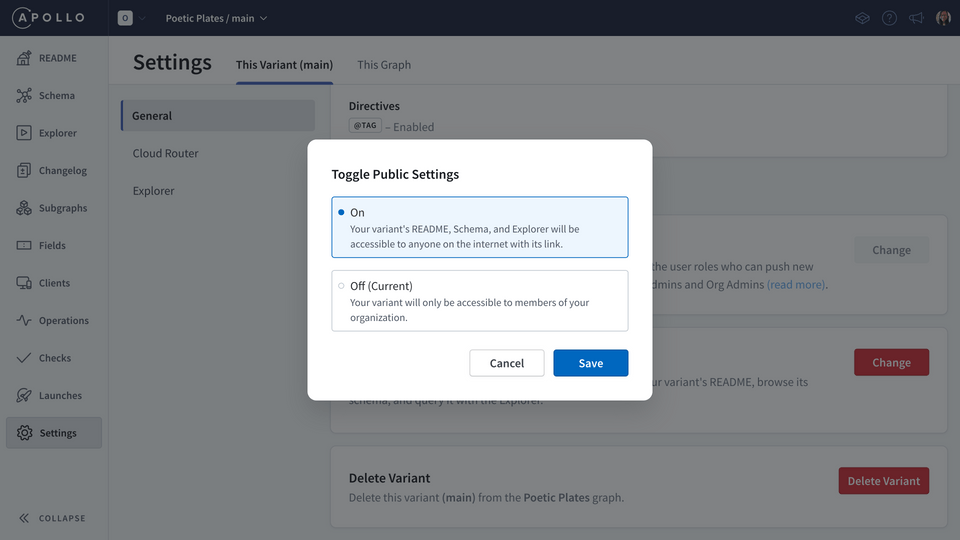
Notice that the header at the top now shows a button labeled "Public". Click on it to navigate to the public version of the supergraph.
In this public version, we have access to view only the four pages we mentioned earlier. We're good to go and we can share this link for other cooking adventurers to explore!
Bonus: Go ahead and edit your supergraph's README! In the README page, click on the pencil icon to edit the README. Include any information that is relevant for developers working with your supergraph. How do you want to introduce them to it? What is important for them to know? What queries can they get started with?
Configuring the cloud router cors options
Next, we need to allow any web-based app consumer to send requests to the supergraph. We want Poetic Plates to be used widely, after all! We'll need to configure the cloud router cors options to enable this.
Back in Studio, in our supergraph's Settings page, under This Variant we'll click on the Cloud Router tab.
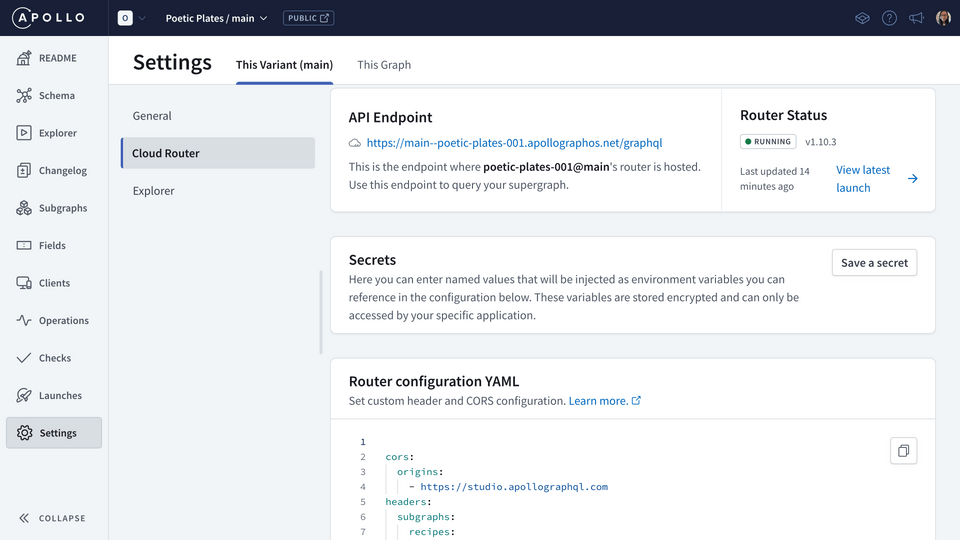
This is where we can configure how the cloud router runs. We've already got some default configuration under the Router Configuration YAML section.
cors:origins:- https://studio.apollographql.comheaders:subgraphs:recipes:request:- propagate:matching: ".*"
The first key, cors contains another key (origins), which contains the list of URLs that are allowed to query the router. Right now, only Studio is allowed to query the router!
We can also see headers configuration for the recipes subgraph, which propagates every single request header. We won't worry too much about that, but we do want to change the cors property!
Let's remove the origins list because we're not going to specify every single origin to allow. Below (still nested within the cors property), we're going to add a new property called allow_any_origin and set it to true.
cors:allow_any_origin: true
Then, hit Save.
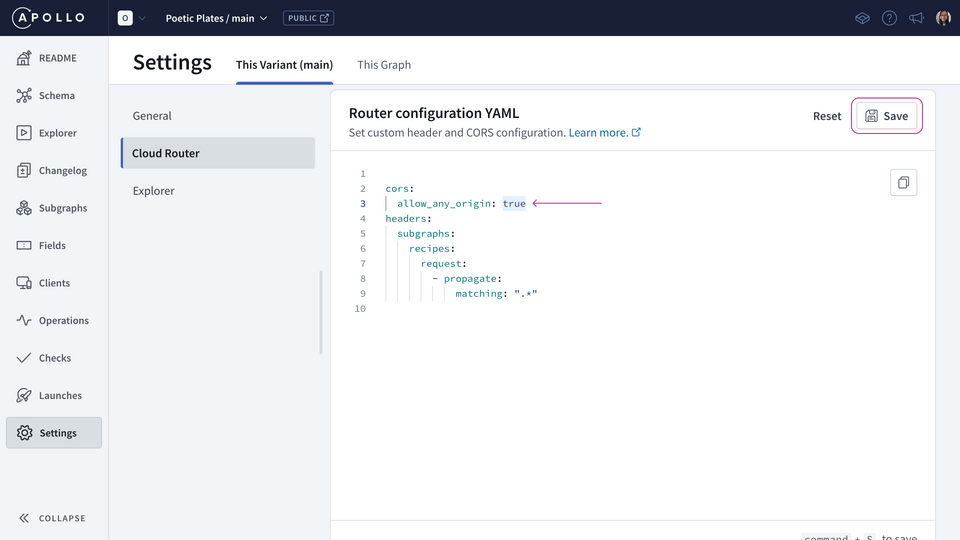
If we didn't set this option, client app developers would see an error in their browser, noting that their localhost or production URL has been blocked by CORS policy.
Practice
Key takeaways
- To enable others to explore and query a public-facing API, you can create a public variant in Studio.
- To enable any web app consumer to connect to your public-facing API, you can configure the cloud router's
corssettings and setallow_any_origintotrue.
Up next
We can share our supergraph to the world, amazing! Now that it's out in the wild, let's learn how we're going to keep an eye on our supergraph's usage.
Share your questions and comments about this lesson
Your feedback helps us improve! If you're stuck or confused, let us know and we'll help you out. All comments are public and must follow the Apollo Code of Conduct. Note that comments that have been resolved or addressed may be removed.
You'll need a GitHub account to post below. Don't have one? Post in our Odyssey forum instead.