Overview
The end is in sight! Let's finish up that field deprecation we started.
In this lesson, we will:
- Inspect field insights in GraphOS
- Learn about two types of field metrics: field executions and referencing operations
- Mark changes as safe for an operation check
- See the CI/CD workflows in action
Inspecting usage for our deprecated field
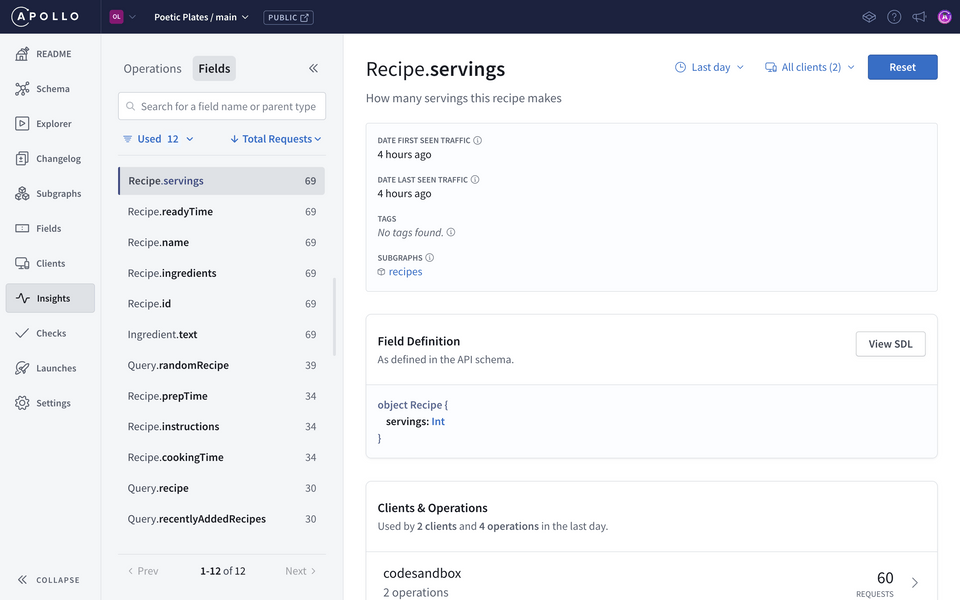
Let's hop over to Studio and navigate to the Insights page, then select the Fields tab.
By default, each field shows the Total requests metric, also known as requesting operations, which is the number of operations in a given period that have included that particular field. You can change this time range using the filters on the page.
This metric helps us see how frequently this particular field is being used, which is exactly what we need to monitor usage for our deprecated field. We want that metric to go all the way down.
Note: There's another type of metric called field executions. To see this metric, you'll need a higher volume of requests being sent to your supergraph. You can learn more about the difference between field executions and requesting operations in the Apollo documentation.
Now, depending on how much time has passed between the last time you sent a query to the supergraph, you might not see any metrics on this page! We're still in tutorial-land, so there isn't much real production traffic going to our supergraph.
Let's go ahead and get some numbers in here so we can walk through what it might look like if we did have more traffic!
The Code Sandbox below contains a script that takes a supergraph URL and sends requests to it over a period of time. We'll use it to send fake traffic to our supergraph.
Go ahead and enter your URL (you can find that at the top of your supergraph's README page). Then press the button to trigger the script!
Note: Right now, our Poetic Plates API does not have any protection against malicious queries or denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. In a future course, we'll cover more techniques to secure your supergraph. In the meantime, you can check out the Apollo technote about the topic to learn more about rate limiting, setting timeouts, pagination and more.
Inspecting field usage
Alright, back to our Fields page!
At the top, let's search for the field
textin our schema.We can see from the field metrics on the Fields page that our deprecated
textfield is still being used. (That's from all the painstaking clicking we just did!).https://studio.apollographql.com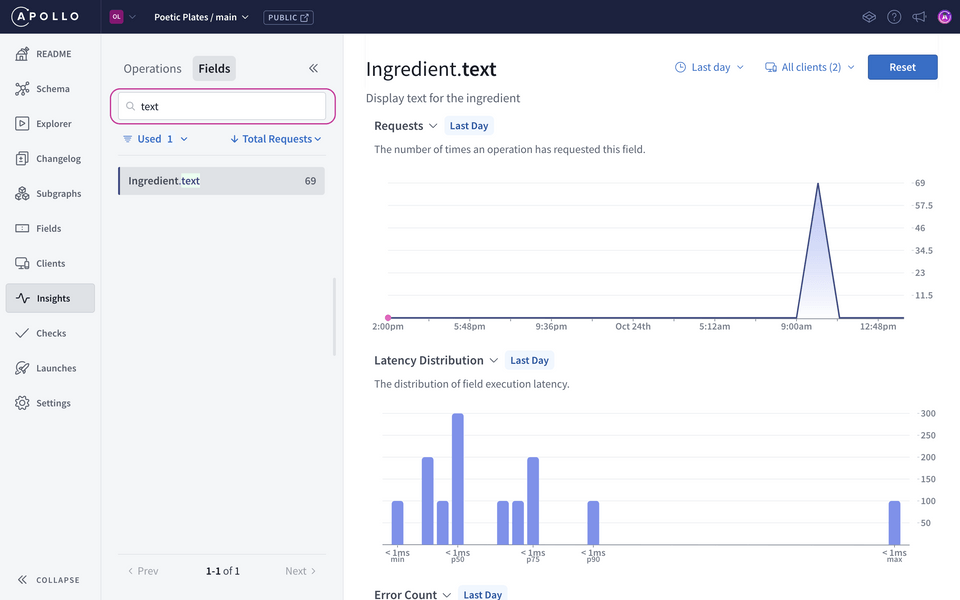
We want to make sure that usage for this field goes down to zero. API consumers should already see a deprecated warning when using this field, but we'll also want to announce it in other channels (such as a dedicated changelog, in a community group, or a targeted email). We'll want to give them enough time to make changes in their API!
Over time, this specific field's usage metrics should trickle downwards. And if it's not? Well, we've got client awareness set up, so we can see exactly which clients aren't following our recommendations! We can reach out to them and encourage them to fix their queries to avoid any breaking changes once we finally remove the field.
Remove a deprecated field
Let's pretend that enough time has passed and we feel ready to remove the field!
Back in the
recipessubgraph repository, open up theschema.graphqlfile.Find the deprecated
textfield in theIngredienttype and remove it.schema.graphql- "Display text for the ingredient"- text: String @deprecated(reason: "Use detailedDescription")What comes after every schema change? A schema check! Run the
rover subgraph checkcommand in your terminal (replacing the parameters below with your own!)rover subgraph check <GRAPH_REF> \--schema <SCHEMA_FILE_PATH> \--name <SUBGRAPH_NAME>Operation checks assess whether the proposed changes to the subgraph will affect any GraphQL operations that have been executed against the schema within a certain timeframe. By default, GraphOS is configured to run checks against operations that have been executed within the last seven days.
If you didn't take a seven-day break between this section and the previous one, it's likely that your operation check failed! 😱
Checking the proposed schema for subgraph recipes against poetic-plates-001@mainCompared 1 schema changes against 7 operations┌────────┬───────────────┬─────────────────────────────────────────┐│ Change │ Code │ Description │├────────┼───────────────┼─────────────────────────────────────────┤│ FAIL │ FIELD_REMOVED │ type `Ingredient`: field `text` removed │└────────┴───────────────┴─────────────────────────────────────────┘View full details at [Studio URL].error[E030]: This operation check has encountered 1 schema change that would break operations from existing client traffic.The changes in the schema you proposed are incompatible with graph poetic-plates-supergraph@main. See https://www.apollographql.com/docs/studio/schema-checks/ for more information on resolving operation check errors.Let's investigate the errors by heading over to Studio's Checks page, then clicking on the most recent check.
Based on historical operations executed against our graph, we see the warning that removing this field might cause a breaking change for clients. In our (pretend) situation, we've made the decision to go ahead with this change! So we can go ahead and override this error.
Operation check: mark changes as safe
Select an operation in the "Affected operation" list. You may have more than one, depending on the queries you've sent to your supergraph that used the
textfield.Click the Override button.
Click Mark changes as safe. This tells the schema checks process that this exact change can be safely ignored in future operation checks.
With the override in place, we can rerun the check right here in Studio, by clicking Rerun check.
This time, the operation check will use the new configurations we've set on this operation, and our removal of the text field will no longer raise the alarm. 🥳
Deploying our changes
Let's get these code and schema changes deployed using our shiny workflows we set up earlier!
Creating a pull request for our changes
In a terminal window, create a new branch. (You can name it whatever you'd like, we'll name ours
remove-ingredient-text.git checkout -b remove-ingredient-textAdd the
schema.graphqlfile we made changes to.git add schema.graphqlCommit the changes.
git commit -m "Remove Ingredient.text field"Then push them up!
git push -u origin remove-ingredient-textWe'll jump back to GitHub to create a pull request for this branch to
main.After creating the pull request, our schema check workflow will trigger automatically. We can click the job to see more details and see our workflow in action.
If the job has passed, we're good to go! We can merge our changes to
mainwith confidence.
Railway deployment
Let's follow our automatic deployment on Railway. Hop over to Railway and check to make sure the deployment is successful!
Publishing to GraphOS
Now that our subgraph server is ready with the changes, we can run our publish schema workflow!
Head back to the GitHub repo and click Actions.
Select the Publish schema workflow from the list of workflows on the left.
Click the Run workflow button, make sure the branch is set to
mainthen click Run workflow to kick off the job.Click the job to see more details and see our workflow in action.
If the job has passed, that means it successfully ran the publish command, so let's check out the launch in Studio to confirm that our changes have landed successfully!
Let's send a query to the supergraph for one last confirmation. Head over to Explorer and run the same query from earlier:
query GetRandomRecipeIngredients {randomRecipe {ingredients {textdetailedDescription}}}
We get an error! Querying for the text field isn't valid anymore, since it's not a part of our schema.
We've successfully removed the field from our schema!
query GetRandomRecipeIngredients {randomRecipe {ingredients {detailedDescription}}}
If we remove the text field, we get the correct data back smoothly 🎉
Practice
Key takeaways
- Requesting operations lists the number of operations in a given period that have included the particular field.
- We can override a failed operation check in Studio.
- Operation checks consider historical operations against the schema to ensure updates to a subgraph do not introduce breaking changes for clients.
Conclusion
You did it! Congratulations on learning how to use GraphOS to safely and confidently launch schema changes with ease 😌
In this course, we covered the specific situation of deprecating a field in our schema. We learned how to use schema checks to identify potential failures before our updates could cause issues in production. We used Rover locally and in our CI/CD pipeline to integrate schema checks and publish our subgraph schema. We also learned how to inspect the results of a schema check and launches in Studio, and how to mark changes as safe for an operation check. The GraphOS schema registry helped us keep track of every single subgraph schema change.
With these tools and knowledge under our belt, we can work on bigger features for Poetic Plates. Why not spice things up by adding another subgraph? In the next course, GraphOS: Growing your API, we'll tackle that and more!
Share your questions and comments about this lesson
Your feedback helps us improve! If you're stuck or confused, let us know and we'll help you out. All comments are public and must follow the Apollo Code of Conduct. Note that comments that have been resolved or addressed may be removed.
You'll need a GitHub account to post below. Don't have one? Post in our Odyssey forum instead.